Table of Contents
China copper imports are a significant topic of discussion as the country ranks sixth in the world for copper reserves yet still heavily depends on importing copper. This paradoxical situation is rooted in a combination of domestic production challenges, increasing demand from key industries, and the strategic importance of copper to China’s economy. In this blog, we’ll explore ten key reasons behind the increasing trend in China’s copper imports and why this reliance is likely to continue.
1. China’s Global Copper Reserve Ranking
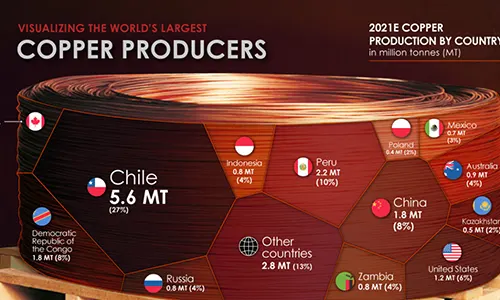
Despite being the sixth-largest holder of copper reserves globally, China’s copper imports continue to rise. With around 34.94 million tons of copper, China’s reserves are significant but still far less than top-ranking Chile, which holds about 190 million tons. This difference in reserves means that even though China is a major copper player, the country must import large amounts of copper to meet its growing needs.
2. The Essential Role of Copper in Industry

The surge in China’s copper imports is largely due to copper’s critical role in modern industries, particularly in sectors like new energy and automotive manufacturing. Copper’s high electrical conductivity makes it indispensable for various applications, from electric motors in vehicles to components in wind turbines and solar panels. The wide-ranging uses of copper in essential technologies drive a constant need for more copper, hence the increase in China copper imports.
3. Rising Demand in the New Energy Sector

One of the main drivers of China copper imports is the booming new energy sector. As the world shifts towards renewable energy, copper has become even more important. For example, the new energy vehicle industry in China consumed about 6 million tons of copper in 2023 alone. Electric vehicles (EVs) require a substantial amount of copper for their motors, batteries, and charging systems, which explains the significant rise in China copper imports.
4. Domestic Production Challenges
The uneven distribution of copper mines across the country and the geological challenges of extraction are major reasons for the continued reliance on China copper imports. The largest copper mines in China, such as the Duolong and Qulong mines in Tibet, are difficult to access and operate in due to harsh environmental conditions. These challenges make domestic production less reliable and more costly, further driving China copper imports.
5. The Quality of Domestic Copper
Another factor contributing to China copper imports is the lower quality of copper found domestically. For example, while Australian copper mines can have purity levels as high as 4.9%, Chinese mines often produce copper with only 2.3% purity. This lower grade means more impurities and less efficient refining processes, making imported copper more appealing, thereby increasing China copper imports.
6. Manufacturing Sector’s Demand
China’s manufacturing sector is another critical factor in the rise of China copper imports. In 2022, manufacturing accounted for 27.7% of China’s GDP, and copper is a key material in this industry. From electronics to heavy machinery, the demand for copper is immense. Even with significant domestic production, the sector’s needs far exceed local supply, pushing China copper imports higher.
7. The Import-Export Paradox
China’s paradoxical situation of being a top copper producer and importer highlights the complex dynamics of China copper imports. In 2022, China consumed 14.69 million tons of refined copper, much of it imported, despite being the largest producer of refined copper. This strategic import approach ensures that China mitigates risks from potential supply chain disruptions, further explaining the continued rise in China copper imports.
8. Copper in Electric Vehicles and Renewable Energy
The rapid growth of the electric vehicle and renewable energy sectors is another reason for the increase in China copper imports. EVs, for example, use about five times more copper than traditional vehicles. The high-voltage DC relays in EVs rely on copper to handle large current flows, making it essential for the functionality of these vehicles and contributing to the rise in China copper imports.
9. Challenges in Finding Copper Substitutes
Given copper’s critical role, finding alternatives is challenging. Research into substitutes continues, but no material matches copper’s combination of conductivity, durability, and cost-effectiveness. This lack of substitutes means that China copper imports will likely continue to grow as the demand for copper remains strong.
10. Future Trends in China Copper Imports
Looking ahead, China copper imports are expected to keep rising. The country is investing in copper mining operations abroad, particularly in Africa and South America, to secure a stable supply. However, the growing demand from sectors like renewable energy, electric vehicles, and high-tech manufacturing will likely keep China copper imports high, even as domestic production tries to catch up.
Conclusion: The Unstoppable Rise of China Copper Imports
The trend of increasing China copper imports reflects the country’s rapid industrial growth, the challenges of domestic production, and the essential role of copper in modern technologies. Despite being a significant copper producer, China’s insatiable demand for this vital metal means that imports will remain a crucial part of the supply chain. As the country continues to develop its new energy and manufacturing sectors, China copper imports are set to keep rising, powering the nation’s future.
Related Links
Top 5 Countries with the Largest Copper Reserves: A Deep Dive into Global Copper Wealth




